Human B2M Knockout Cell Line-K562
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2725
Host Cell: K562 Target Gene: B2M
Size: 2x10^6 cells/vial Validation: Sequencing
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2725
Host Cell: K562 Target Gene: B2M
Size: 2x10^6 cells/vial Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT2725 |
| Cell Line Information | This cell line is a stable cell line with a homozygous knockout of human B2M using CRISPR/Cas9. |
| Target Gene | B2M |
| Gene ID | 567 |
| Genotype | B2M (-/-) |
| Host Cell | K562 |
| Cell Type | Hematopoietic |
| Size | 2x10^6 cells/vial |
| Sequencing Result | Homozygous: 1 bp deletion in exon |
| Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Media Type | Cells were cultured in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. |
| Subcultivation Ratio | Split saturated culture every 2-3 days |
| Culture Condition | Cells are cultured at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO<sub>2</sub>. |
| Freeze Medium | 70% RPMI1640 + 20% FBS + 10% DMSO |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
The human K562 leukemia cell line, used as a scaffold for artificial antigen-presenting cells (aAPCs) for in vitro lymphocyte expansion, normally does not express major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. However, when stimulated with human T lymphocyte culture supernatant, K562 cells upregulate beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) and MHC class I expression, thereby inducing allo-specific T cells. Here, researchers disrupted the B2M locus in K562 cells by CRISPR/Cas9 and obtained MHC class I-negative K562 cells. A K562-based MHC class I-negative aAPC line was further generated by zinc finger nuclease-mediated insertion of costimulatory molecules into the AAVS1 locus. This aAPC line can attenuate allogeneic immune responses but supports robust antigen-independent and CD19 antigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor-T cell expansion in vitro. These results suggest that B2M-knockout K562 cells provide a new scaffold for the construction of aAPCs and their broader application in adoptive immunotherapy.
K562 cells are commonly used as feeder cells for large-scale expansion of αβ-T cells. To test the stimulating function of B2M knockout K562-based aAPCs for antigen-independent T-cell expansion, PBMCs were treated with CD3/CD28 antibody-coated micro-Dynabeads for 1 week to activate T cells. T cells were then collected to mix with inactivated K562B or K562A cells at an 1:50 ratio and expanded in the presence of anti-CD3 antibody, OKT-3, for 2 weeks (Figure 1A). With this method, a total cell expansion of 1000- to 2000-fold was observed at the end of the 14-day culture in a representative study (Figure 1B). The researchers further investigated the composition of the cell population after 2 weeks of expansion (Figure 1C). The CD8+ αβ-T-cell population constituted the major portion (60–75%) followed by the CD4+ αβ-T-cell population (20–40%). CD3- CD56+ NK cells percentage was slightly increase from 3 to 13% during Dynabeads stimulation due to the loss of monocytes and other non-T/NK lymphocytes, but a decrease in the proportion of NK cells from 3 to 5% was observed during the 14-day T cell/K562 coculture. There was no obvious expansion of the γδ-T-cell population (1.5–3%). These studies suggest that B2M knockout in K562 does not affect its ability to function as aAPC for antigen-independent T cell expansion.
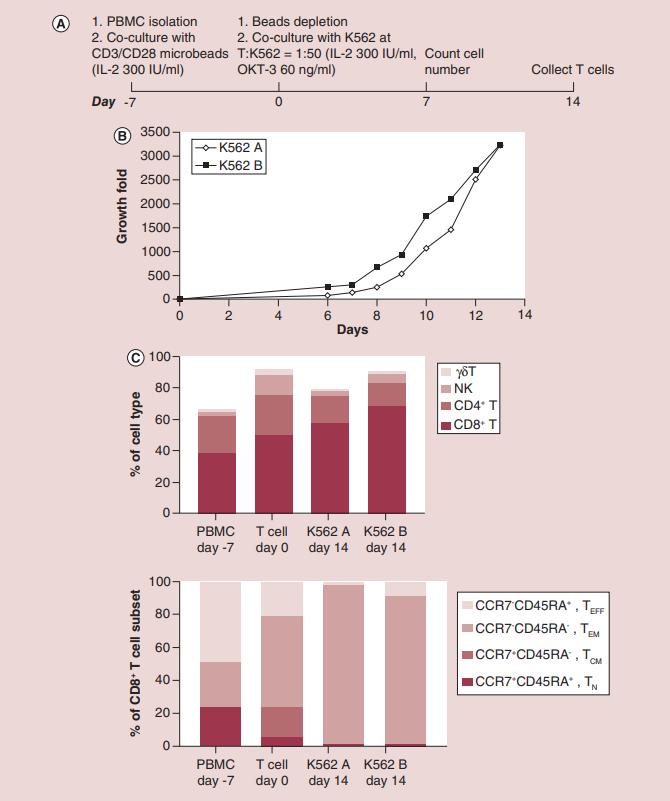 Figure 1. Antigen-independent T-cell expansion with β-2 microglobulin-knockout K562-based artificial antigen presenting cells. (Zha S, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Antigen-independent T-cell expansion with β-2 microglobulin-knockout K562-based artificial antigen presenting cells. (Zha S, et al., 2019)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER