Human EGFR Knockout Cell Line-A549
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2588
Host Cell: A549 Target Gene: EGFR
Size: 2x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2588
Host Cell: A549 Target Gene: EGFR
Size: 2x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT2588 |
| Cell Line Information | This cell line is a stable cell line with a homozygous knockout of human EGFR using CRISPR/Cas9. |
| Target Gene | EGFR |
| Gene ID | 1956 |
| Genotype | EGFR (-/-) |
| Host Cell | A549 |
| Cell Type | Epithelial |
| Size | 2x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL |
| Sequencing Result | 1 bp deletion in exon |
| Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Media Type | Cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. |
| Growth Properties | Cells are cultured as a monolayer at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Split at 80-90% confluence, approximately 1:3-1:5. |
| Freeze Medium | Complete medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) DMSO |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) are immune checkpoint proteins expressed in T cells. Here, researchers found that CTLA4 is expressed in a subset of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and a subpopulation of cancer cells within lung cancer tissues. It was further found that in NSCLC cells, anti-CTLA4 antibodies can induce PD-L1 expression, which is mediated by CTLA4 and the EGFR pathway involving MEK and ERK phosphorylation. Anti-CTLA4 antibodies failed to induce PD-L1 expression in NSCLC cells in the presence of CTLA4 knockout cells, EGFR knockout cells, or in the presence of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. In addition, in the absence of adaptive immunity, anti-CTLA4 antibodies promoted NSCLC cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. These results suggest that tumor cell-intrinsic CTLA4 can regulate PD-L1 expression and cell proliferation, and that anti-CTLA4 antibodies, by binding to tumor cell-intrinsic CTLA4, may lead to activation of the EGFR pathway in cancer cells.
According to the study, both CTLA4 and PD-L1 are expressed at higher levels in EGFR wild-type or EGFR activating mutation NSCLC cells, and the researchers focused on determining the EGFR activation status. The study found that after anti-CTLA4 antibody treatment, phosphorylated EGFR (pEGFR) levels did increase in a dose-dependent manner, while total EGFR levels did not change (Figure 1A). On the other hand, IFN-γ treatment did not change pEGFR levels (Figure 1A). To further confirm this finding, the researchers examined the levels of phosphorylated MEK (pMEK) and phosphorylated ERK (pERK), downstream components of EGFR. The results showed that anti-CTLA4 also increased pMEK and pERK levels in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1B). In contrast, IFN-γ increased the levels of phosphorylated S6 ribosomal protein (pS6) without changing the levels of pMEK and pERK (Figure 1B). In addition, the EFGR inhibitor canertinib suppressed pEGFR levels and also suppressed anti-CTLA4-induced PD-L1 expression levels (Figure 1C, lane 4). Notably, canertinib had no effect on IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression (Figure 1C, lane 3). In A549 EGFR knockout (KO) cells, anti-CTLA4 failed to induce PD-L1 expression (Figure 1D, lane 6), while IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression was intact (Figure 1D, lane 5). In A549 CTLA4 KO cells, anti-CTLA4-induced PD-L1 upregulation was also attenuated (Figure 1D, lane 9). Similarly, IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression was intact (Figure 1D, lane 8).
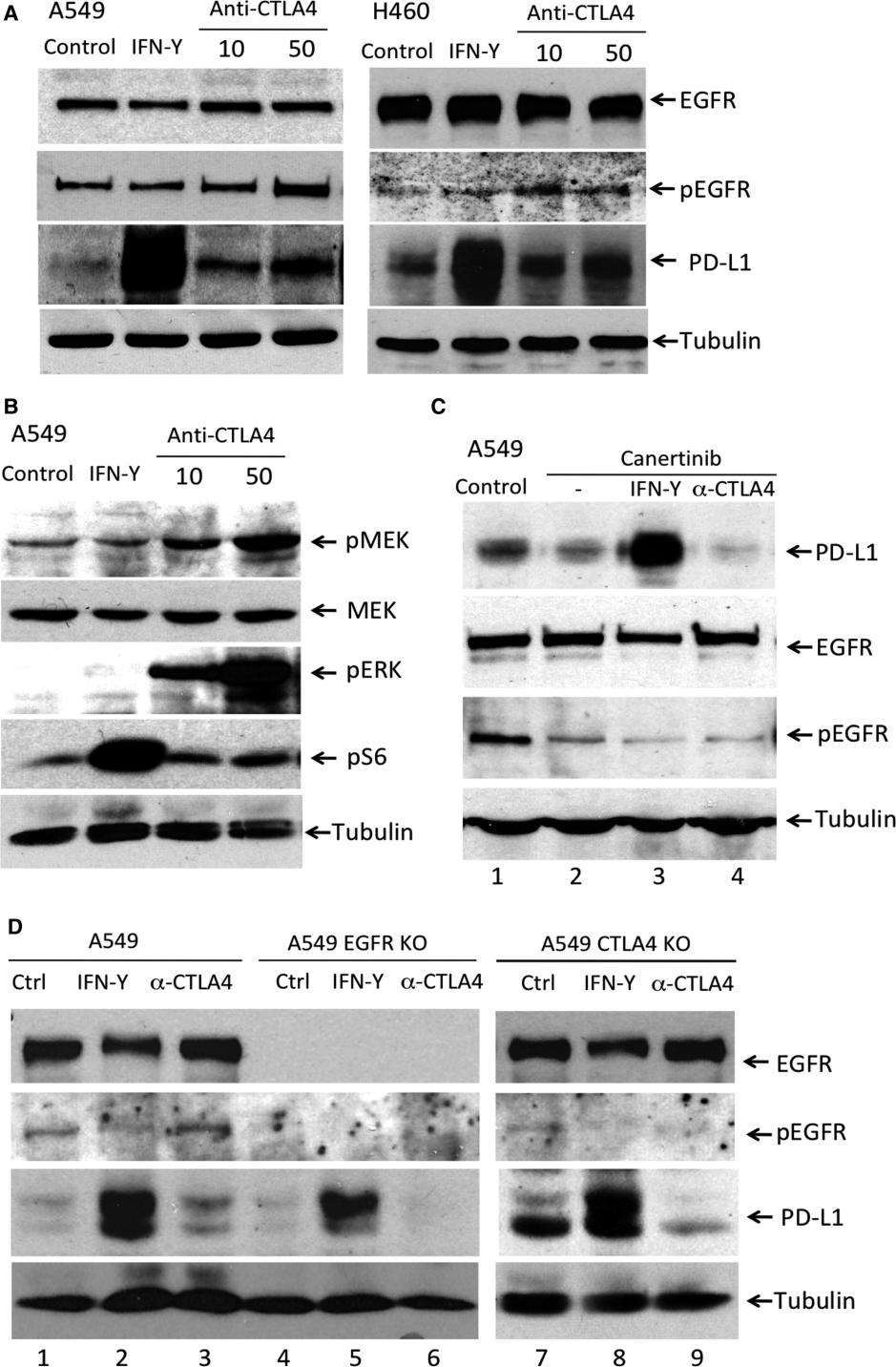 Figure 1. Anti-CTLA4 induced PD-L1 expression is EGFR pathway dependent in NSCLC cells. (Zhang H, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Anti-CTLA4 induced PD-L1 expression is EGFR pathway dependent in NSCLC cells. (Zhang H, et al., 2019)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER