Human PIEZO1 Knockout Cell Line-HEK293T
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2661
Host Cell: HEK293T Target Gene: PIEZO1
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
Cat.No. : CSC-RT2661
Host Cell: HEK293T Target Gene: PIEZO1
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT2661 |
| Cell Line Information | This cell is a stable cell line with a homozygous knockout of human PIEZO1 using CRISPR/Cas9. |
| Target Gene | PIEZO1 |
| Host Cell | HEK293T |
| Size Form | 1 vial (10^6 cell/vial) |
| Shipping | Dry ice package |
| Storage | Liquid nirtogen |
| Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Media Type | Cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. |
| Growth Properties | Cells are cultured as a monolayer at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Split at 80-90% confluence, approximately 1:3-1:6. |
| Freeze Medium | Complete medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) DMSO |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
Mechanosensitive channels are integral membrane proteins that sense mechanical stimuli. Like most plasma membrane ion channel proteins, they must undergo biogenesis quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum before reaching their destination at the plasma membrane. Studies here demonstrate that N-linked glycosylation of two highly conserved asparagine residues in the 'cap' region of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is essential for the mature protein to reach the plasma membrane. Both mutation of these asparagines (N2294Q/N2331Q) and treatment with an enzyme that hydrolyzes N-linked oligosaccharides (PNGaseF) abolished the fully glycosylated mature Piezo1 protein. N-glycans in the cap are a prerequisite for N-glycosylation of the 'propeller' region, which is present in a loop essential for mechanotransduction. Importantly, trafficking-defective Piezo1 variants associated with systemic lymphoid dysplasia and bicuspid aortic valves showed reduced fully N-glycosylated Piezo1 protein. Thus, in vitro N-linked glycosylation status correlates with efficient membrane trafficking and will help determine the functional impact of Piezo1 variants of unknown significance.
In this study, negative pressure was applied to cell-attached patches of transiently transfected Piezo1 knockout HEK293T cells using a high-speed pressure clamp. Both single mutants exhibited normal stretch-activated responses (Figure 1a, b), consistent with the two bands on the western blot. Given the strong evidence that the cap is involved in Piezo1 inactivation, the researchers tested whether inactivation was altered, but neither Asn to Gln mutant affected the inactivation time constant in the cell-attached patch (Figure 1c). However, the N2294Q/N2331Q mutant had almost no stretch-activated current (Figure 1a, b), indicating that the FG Piezo1 protein represents a pool of membrane proteins.
In addition, the researchers confirmed the trafficking defect using a combination of nanogold immunolabeling and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with Piezo1 knockout HEK293T cells. Micrographs clearly showed that WT Piezo1 had reached the plasma membrane, whereas the N2294Q/N2331Q double mutant had little or no membrane labeling (Figure 1d). Quantification of the ratio of membrane to intracellular nanogold staining for Piezo1 and N2294Q/N2331Q showed a significant reduction in membrane labeling for N2294Q/N2331Q, consistent with a trafficking defect (Figure 1e). Nano-gold labelling was not seen in un-transfected Piezo1 knockout HEK293T cells.
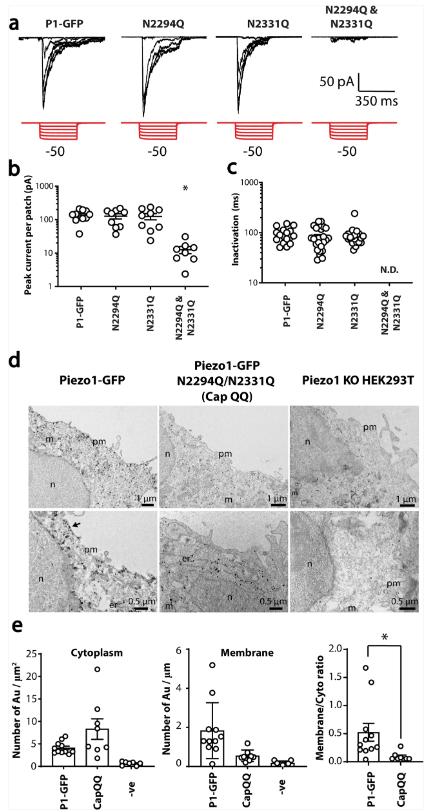 Figure 1. Effect of mutation of N2294 and N2331 on mechanically induced gating of Piezo1. (Li J V, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Effect of mutation of N2294 and N2331 on mechanically induced gating of Piezo1. (Li J V, et al., 2021)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER