Cas9 Stable Cell Line - HCT116
Cat.No. : CSC-RO0222 Host Cell: HCT116
Size: >1x10^6 cells/vial Validation: T7 Endonuclease I assay
Cat.No. : CSC-RO0222 Host Cell: HCT116
Size: >1x10^6 cells/vial Validation: T7 Endonuclease I assay
| Cat. No. | CSC-RO0222 |
| Product Type | Cas9 overexpression stable cell line |
| Introduction | Clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 is a gene-editing technology that contains two essential components: a guide RNA (gRNA) to match a target gene, and the Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) endonuclease which causes a double-stranded DNA break, allowing modifications to the genome via nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). |
| Cell Line Information | HCT116-Cas9 cell line is engineered to stably overexpress Cas9 nuclease. The Cas9 nuclease in HCT116-Cas9 cell line has been functionally validated using T7 Endonuclease I assay. In combination with separately transfected sgRNAs, HCT116-Cas9 cell line can be used to efficiently generate targeted genomic modifications including gene knockout, gene knockin, gene mutagenesis, gene tagging etc. It is also an ideal cell line model for sgRNA screening and validation, either individually or in pools. |
| Target Gene | Cas9 |
| Host Cell | HCT116 |
| Applications | 1) CRISPR genome editing, such as gene knockout (KO), gene knockin (KI), gene mutagenesis, gene tagging etc. 2) High-throughput sgRNA screening and validation |
| Quality Control | 1) T7E1 assay 2) Mycoplasma detection |
| Size Form | One vial of frozen cells, typically >1x10^6 cells/vial |
| Shipping | Dry ice |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
The researchers used an auxin-inducible degradation system to create a Cas9 stable cell line, the HCT116 cell line, that can quickly eliminate ORC2, revealing a variety of cell division cycle phenotypes. First, the researchers found that each subunit of ORC and CDC6 is essential in human cells through tiling-sgRNA CRISPR screening. Then, the researchers observed in these stable cell lines that in the absence of ORC2, the cells' ability to load MCM2-7 on G1 phase chromatin was weakened, resulting in difficulties in initiating DNA replication or the inability of the cell division cycle to proceed normally. In addition, ORC2-deficient cells have larger nuclei and decompressed heterochromatin. Some ORC2-deficient cells that completed DNA replication entered mitosis but never exited. ORC1 knockout cells also exhibited extremely slow cell proliferation rates and abnormal cell and nuclear morphology. Therefore, ORC proteins and CDC6 are essential for normal cell proliferation and nuclear organization.
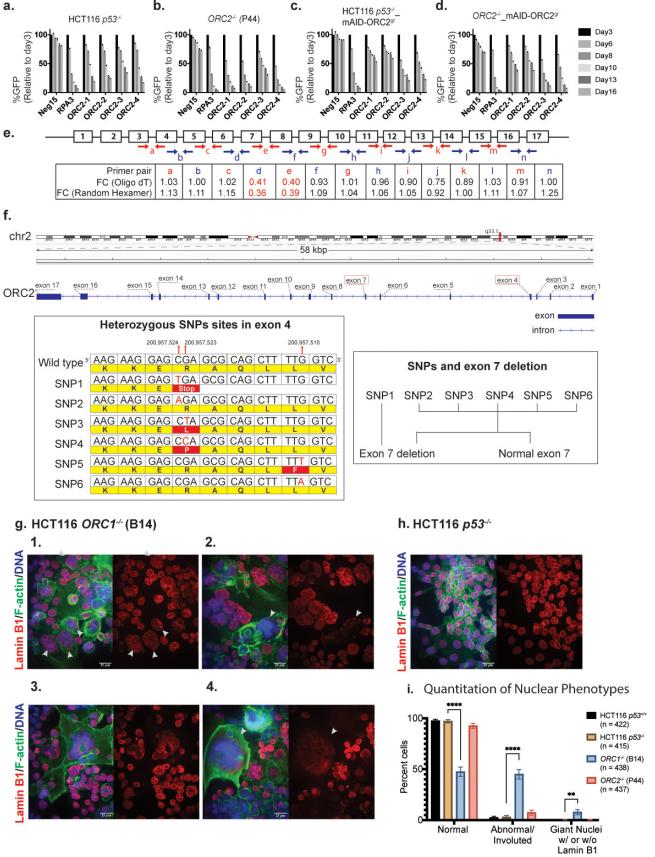 Figure 1. Using tilling-sgRNA CRISPR screening, the researchers found that each subunit of ORC and CDC6 is essential in human cells. Through the auxin-induced degradation system, they created a Cas9 stable cell line that can rapidly eliminate ORC2, revealing a variety of cell division cycle phenotypes. The main defect of ORC2 deficiency is that cells encounter difficulties in initiating DNA replication or blocked cell division cycle progression in the G1 phase, resulting in reduced loading of MCM2-7 on chromatin. (Chou HC, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Using tilling-sgRNA CRISPR screening, the researchers found that each subunit of ORC and CDC6 is essential in human cells. Through the auxin-induced degradation system, they created a Cas9 stable cell line that can rapidly eliminate ORC2, revealing a variety of cell division cycle phenotypes. The main defect of ORC2 deficiency is that cells encounter difficulties in initiating DNA replication or blocked cell division cycle progression in the G1 phase, resulting in reduced loading of MCM2-7 on chromatin. (Chou HC, et al., 2021)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER