Human FBXW7 Knockout Cell Line-DLD-1
Cat.No. : CSC-RT0018
Host Cell: DLD-1 Target Gene: FBXW7
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
Cat.No. : CSC-RT0018
Host Cell: DLD-1 Target Gene: FBXW7
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT0018 |
| Cell Line Information | DLD-1-FBXW7 (-/-) is a cell line with a homozygous knockout of human FBXW7 |
| Target Gene | FBXW7 |
| Host Cell | DLD-1 |
| Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
The tumor suppressor p53 plays a key role in integrating multiple stress responses. Therefore, p53 levels are precisely regulated by multiple ubiquitin ligases. In the study, researchers found that FBXW7, a substrate recognition component of the SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) E3 ligase, interacts with p53 and targets p53 for polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation after exposure to ionizing radiation or etoposide. Mechanistically, DNA damage activates ATM to phosphorylate p53 on Ser33 and Ser37, thereby promoting FBXW7 binding and subsequent degradation of p53 by SCFFBXW7. Inactivation of ATM or SCFFBXW7 by small molecule inhibitors or genetic knockdown/knockout approaches prolongs p53 protein half-life after DNA damage in an MDM2-independent manner. Biologically, FBXW7 inactivation stabilizes p53 to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, thereby sensitizing cancer cells to radiation or etoposide. In conclusion, this study elucidates the mechanism by which FBXW7 confers cancer cell survival during radiotherapy or chemotherapy through p53 targeting.
In HCT116 FBXW7 knockout cells, ectopic expression of wild-type FBXW7, but not FBXW7-ΔF or R479L mutants, accelerated the turnover of p53 by shortening its protein half-life (Figure 1B). Since polyubiquitination is required for proteins destined for degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), researchers next examined whether FBXW7 promoted polyubiquitination of p53 using an in vivo ubiquitination assay. Indeed, researchers found that FBXW7 promoted polyubiquitination of ectopically expressed p53 in H1299 cells in which MDM2 had been depleted by CRISPR-Cas9 (Figure 1C). Direct immunoblotting (IB) showed that polyubiquitination of endogenous p53 was also consistently reduced in FBXW7 knockout or FBXW7-depleted cells (Figure 1D). Finally, polyubiquitination of FLAG-p53(S33D/S37D) was readily detected in an in vitro ubiquitination assay in the presence of E1, E2, and SCFFBXW7, but not the SCFFBXW7-ΔF complex in the presence of E3 (Figure 1E). Taken together, these results suggest that FBXW7 targets p53 for polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation via the UPS.
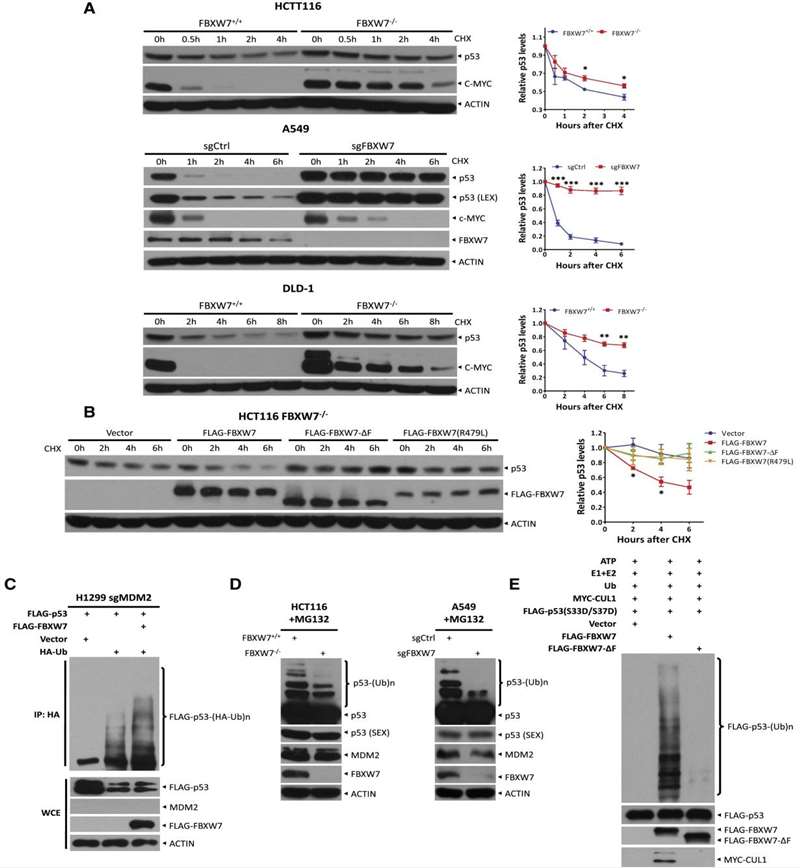 Figure 1. FBXW7 Shortens the p53 Half-Life and Promotes p53 Ubiquitination. (Cui D, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. FBXW7 Shortens the p53 Half-Life and Promotes p53 Ubiquitination. (Cui D, et al., 2020)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER