BRD3 Knockout Cell Line-293T
Cat.No. : CSC-RT0456
Host Cell: 293T Target Gene: BRD3
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
Cat.No. : CSC-RT0456
Host Cell: 293T Target Gene: BRD3
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT0456 |
| Cell Line Information | 293T-BRD3 (-/-) is a stable cell line with a homozygous knockout of human BRD3 |
| Target Gene | BRD3 |
| Host Cell | 293T |
| Host Cell Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
As members of the bromodomain and extra-terminal motif protein families, bromodomain-containing proteins regulate a variety of biological processes, including protein scaffolding, mitosis, cell cycle progression, and transcriptional regulation. The roles of these bromodomain proteins (Brds) in the innate immune response have been reported, but the role of Brd3 remains unclear. Researchers found that viral infection significantly downregulated Brd3 expression in macrophages, and Brd3 knockout inhibited virus-induced IFN-β production. Brd3 interacts with IRF3 and p300, increases p300-mediated IRF3 acetylation, and enhances the binding of IRF3 to p300 upon viral infection. Importantly, Brd3 promotes the recruitment of the IRF3/p300 complex to the Ifnb1 promoter and increases the acetylation of histone 3/histone 4 within the Ifnb1 promoter, thereby enhancing type I interferon production. Thus, these studies suggest that Brd3 may act as a coactivator for IRF3/p300 transcriptional activation of Ifnb1 and provide new insights into epigenetic mechanisms for efficient activation of innate immune responses.
Here, the researchers performed ChIP analysis to evaluate the effect of Brd3 on the recruitment of IRF3 and p300 to the Ifnb1 promoter. As shown in Figure 1a, virus-induced IRF3 and p300 binding to the Ifnb1 gene promoter was significantly reduced in Brd3 knockout (Brd3-ko) cells, indicating that Brd3 enhanced the virus-triggered recruitment of IRF3 and p300 to the Ifnb1 promoter. When Brd3 protein was knocked out, acetylated histone 3 and histone 4 within the Ifnb1 promoter were significantly reduced compared with control cells after virus infection (Figure 1b). However, the acetylation of histone 3 and histone 4 within the Tnfa promoter was not different between Brd3 knockout cells and control cells. Taken together, these results indicate that Brd3 promotes the transcriptional activity of IRF3/p300 by enhancing virus-triggered IRF3/p300 recruitment to the Ifnb1 promoter and assisting the acetylation of histone 3 and histone 4, thereby promoting the production of type I interferons.
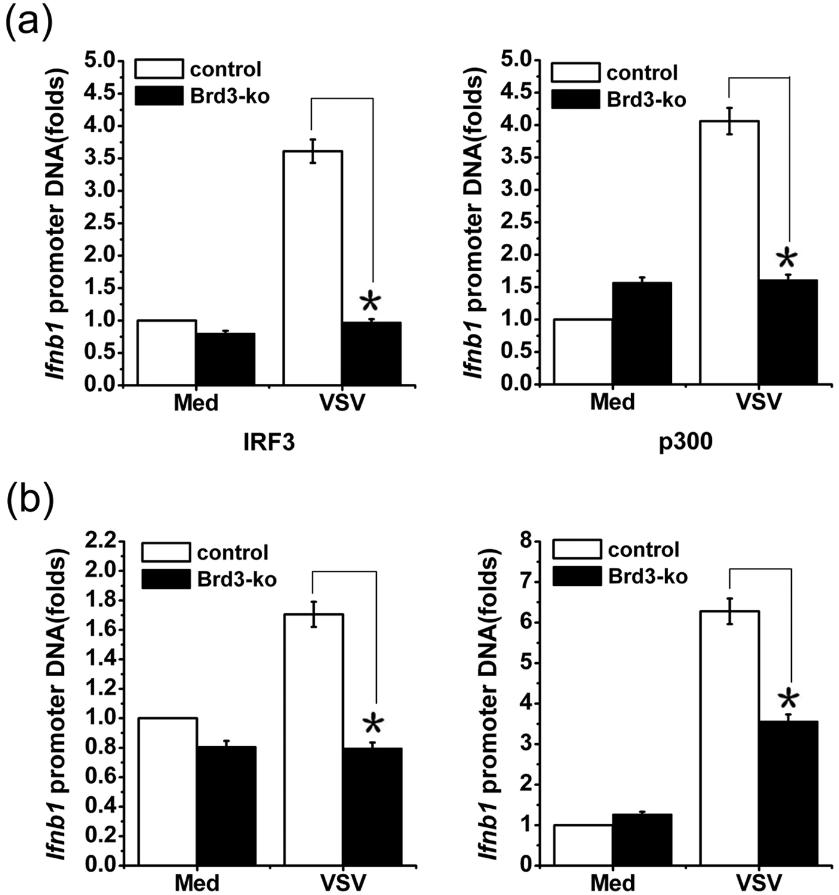 Figure 1. Brd3 recruits IRF3/p300 complex to the promoter of Ifnb1 and facilitates the transcription of Ifnb1. (Ren, Wenhui, et al. 2017)
Figure 1. Brd3 recruits IRF3/p300 complex to the promoter of Ifnb1 and facilitates the transcription of Ifnb1. (Ren, Wenhui, et al. 2017)

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER